Temporary Employee
What is a temporary employee?
A temporary employee, often referred to as a “temp”, is an individual hired by a company for a specific period or project rather than on a permanent basis. Their employment typically has a defined start and end date, which may be determined by the duration of a project, seasonal demands, or to fill in for a regular employee who is temporarily unavailable (e.g., on leave).
Temporary employees may work full-time or part-time and are often contracted through a staffing agency, although some are hired directly by the employer. Depending on the company’s policies and local labor laws, they may or may not receive the same benefits as permanent employees. Temporary roles can serve as a way for individuals to gain experience, earn income in the short term, or transition into a permanent position.
Reasons for hiring temporary employees
Hiring temporary employees can address various organizational needs and challenges. Here are some common reasons companies have to hire temporary staff:
- Seasonal demand: Industries like retail, hospitality, or agriculture experience peak seasons that temporarily require additional workers.
- Project-based work: These employees are useful for short-term projects or specialized tasks that don’t justify hiring full-time workers.
- Cost-effectiveness: Temporary workers can be a cost-saving option, as companies typically don’t need to provide them with benefits like health insurance or retirement contributions.
- Staffing gaps: Temporary employees employees can cover permanent employees’ absences for reasons such as parental leave, extended sick leave, or vacations.
- Specialized expertise: Temporary staff can contribute niche skills or knowledge for a defined period without long-term employment obligations.
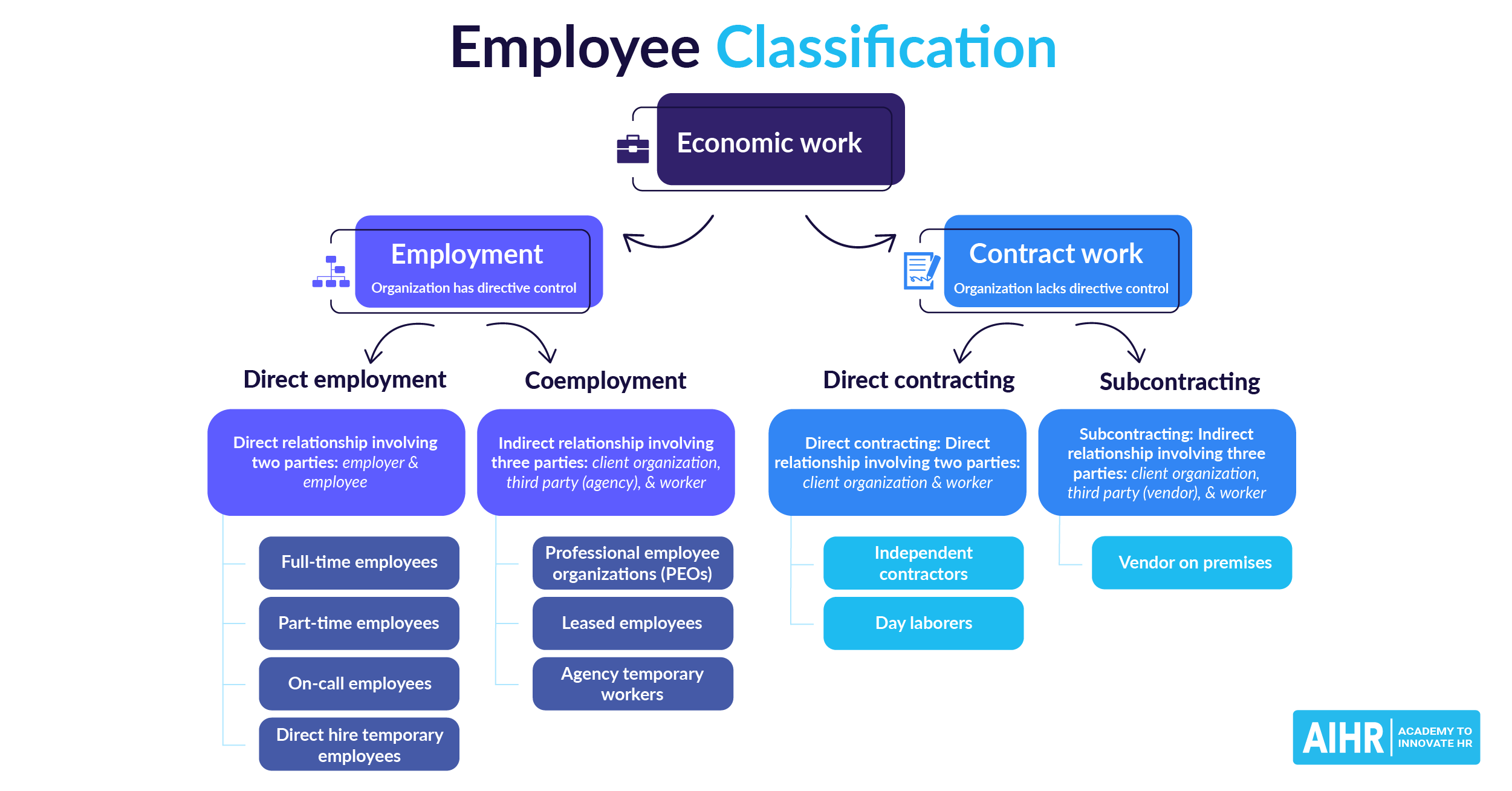
Temporary employee vs. contractor
A temporary employee and a contractor are both non-permanent workers, but they differ in how they are classified, managed, and compensated. Here’s a breakdown of the key distinctions between the two:
Definition
Hired by a company for a limited period or specific task.
Self-employed or working through a third party for a client.
Considered an employee of the company or staffing agency.
Independent worker, not considered an employee.
Employee benefits
May receive benefits like sick leave, health insurance, or holiday pay (varies by company).
Generally does not receive benefits from the client company.
Tax withholding
Employer withholds taxes and contributes to Social Security and Medicare.
Contractor handles their own taxes and self-employment contributions.
Seasonal vs. temporary employee
A seasonal employee is hired during specific times of the year to manage predictable, recurring workloads, such as holiday seasons or summer months. Common in industries like retail and agriculture, their employment ends when the peak period does. While basic labor laws cover them, seasonal employees often don’t qualify for benefits due to the short-term nature of their roles.
A temporary employee, on the other hand, is hired for short-term needs not tied to any specific season, such as covering for someone on leave or assisting with a project. Their employment has a defined end date but is more flexible than seasonal roles, depending on the employer’s immediate requirements.

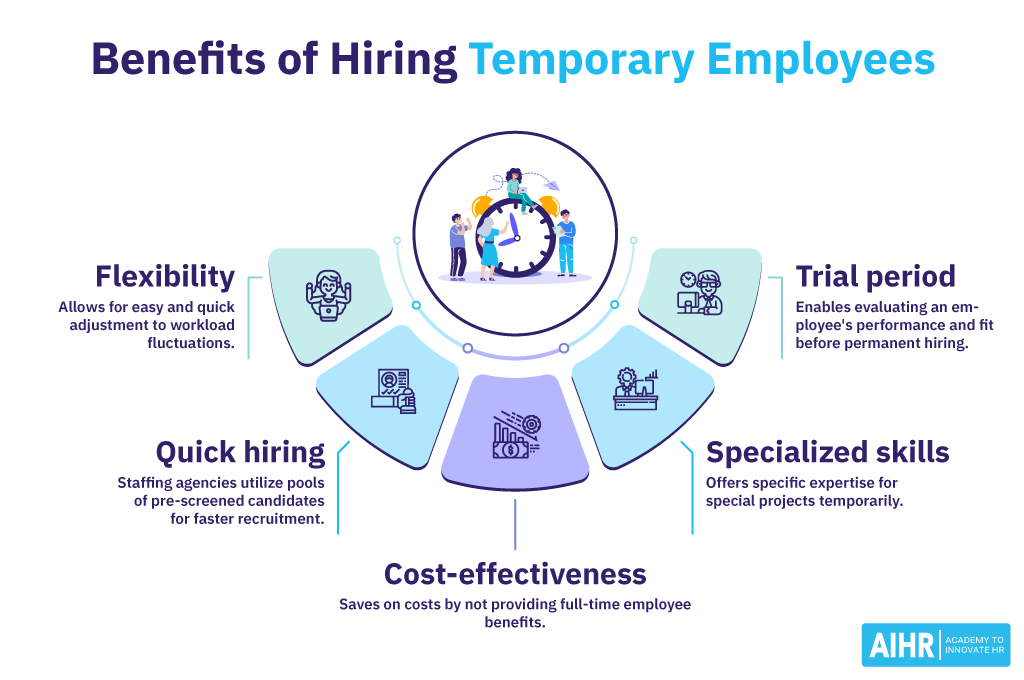
What are the benefits of hiring temporary employees?
Hiring temporary employees can offer several business advantages:
- High flexibility: Temporary workers allow businesses to adjust more easily and quickly to workload fluctuations. This is particularly beneficial in sectors with seasonal peaks or specific project needs.
- Quick hiring process: Temporary staffing agencies often have pools of pre-screened candidates ready to work, which can significantly reduce the time to fill a position.
- Cost-effectiveness: Employing temporary employees can allow businesses to avoid the high costs associated with full-time employees, such as health benefits, paid leave, and other full-time employee-related expenses.
- Specialized skills: Temporary workers can be brought in for special projects requiring specific skills or expertise unavailable within the current workforce.
- Trial period: Hiring temporary employees allows the employer to evaluate the worker’s performance and fit within the company culture before committing to hiring them permanently.
How to hire a temporary employee: 7 steps
HR can hire a temporary employee either directly or through a staffing agency. Here is a step-by-step guide to hiring a temporary employee:
- Determine your needs: Clearly define job responsibilities, necessary skills, and employment duration to target suitable candidates and set clear expectations.
- Understand temporary employee rights and laws: Learn about the legal requirements for temporary employment, including equal pay, working hours, health and safety, and anti-discrimination laws, to ensure compliance and fair treatment.
- Source candidates: Use internal resources, job boards, social media, and staffing agencies to find qualified candidates. Staffing agencies can help manage legal and payroll issues efficiently.
- Conduct thorough interviews: Thoroughly screen candidates to make sure they meet job requirements. Conduct interviews to evaluate skills, motivation, and cultural fit, and clearly discuss the temporary nature of the role.
- Offer and negotiation: Present a clear offer detailing the terms of employment, ensuring it complies with temporary employee laws and regulations.
- Manage performance: Continuously manage and provide feedback on performance, addressing any issues promptly to maintain productivity and morale.
- End of assignment procedures: Evaluate the employee’s performance and determine if there’s an opportunity to extend their contract, offer them a permanent position, or conclude as planned. If the assignment is ending, ensure a smooth offboarding process.
FAQ
Temporary employees typically work varied hours depending on the employer’s needs and the nature of the job. Some may work part-time, while others may have full-time schedules, but their assignments are usually short-term. Employers should specify hours in the job description or contract.
The transition from temporary to permanent employment depends on the organization’s policies and priorities, applicable labor laws, and both parties’ interest in a long-term engagement. This change typically requires a formal evaluation of the employee’s performance, an ongoing need for the role, and possibly a new employment contract.
The cost of hiring a temporary employee varies widely, factoring in staffing agency fees, hourly wages, and any related taxes or benefits. Agency fees can significantly increase costs, often adding 25% to even 100% to the employee’s pay rate. The total expense also depends on the industry, job role, and geographical location.