What is AI in HR?

Artificial intelligence (AI) in HR refers to the use of technologies such as machine learning (ML), predictive analytics, and natural language processing (NLP) to help automate and perform HR tasks that typically require human judgment.
For example, HR practitioners and teams can use AI to streamline recruitment, payroll, and benefits administration, draft policy documents and contracts, and provide real-time HR support to employees. It also enables data-driven decision-making for training, retention, and workforce planning while helping to reduce bias and improve the experience for both candidates and employees.
AI can be applied on multiple levels, with individuals, the HR team, and the organization as a whole, with different benefits and risk levels.
For example, at the individual level, AI helps to save time and improve quality with low risk. At the team level, AI complements existing skills, collaborating to improve workflows and processes with more complex but manageable risks. At the enterprise level, AI supports large-scale decision-making that impacts business strategy, but the stakes and potential risks are much higher.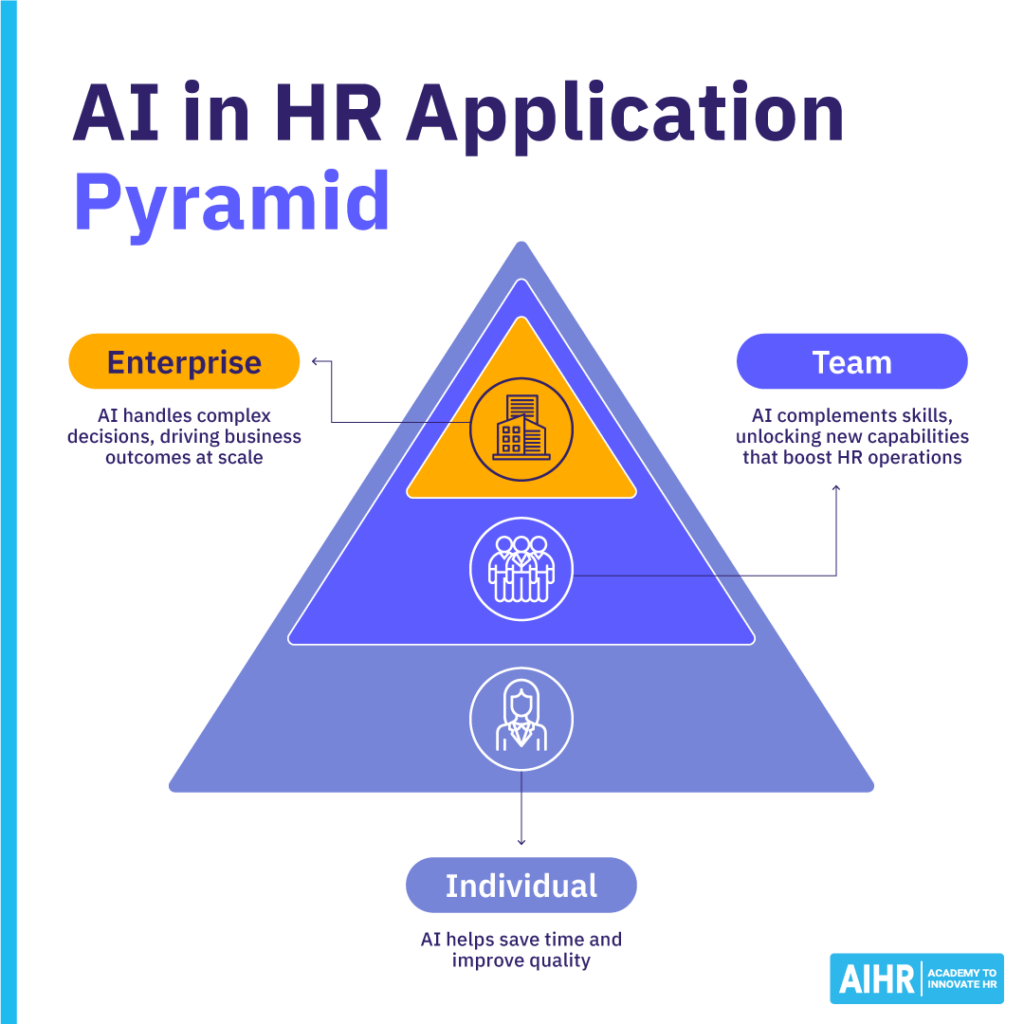
Types of AI in HR

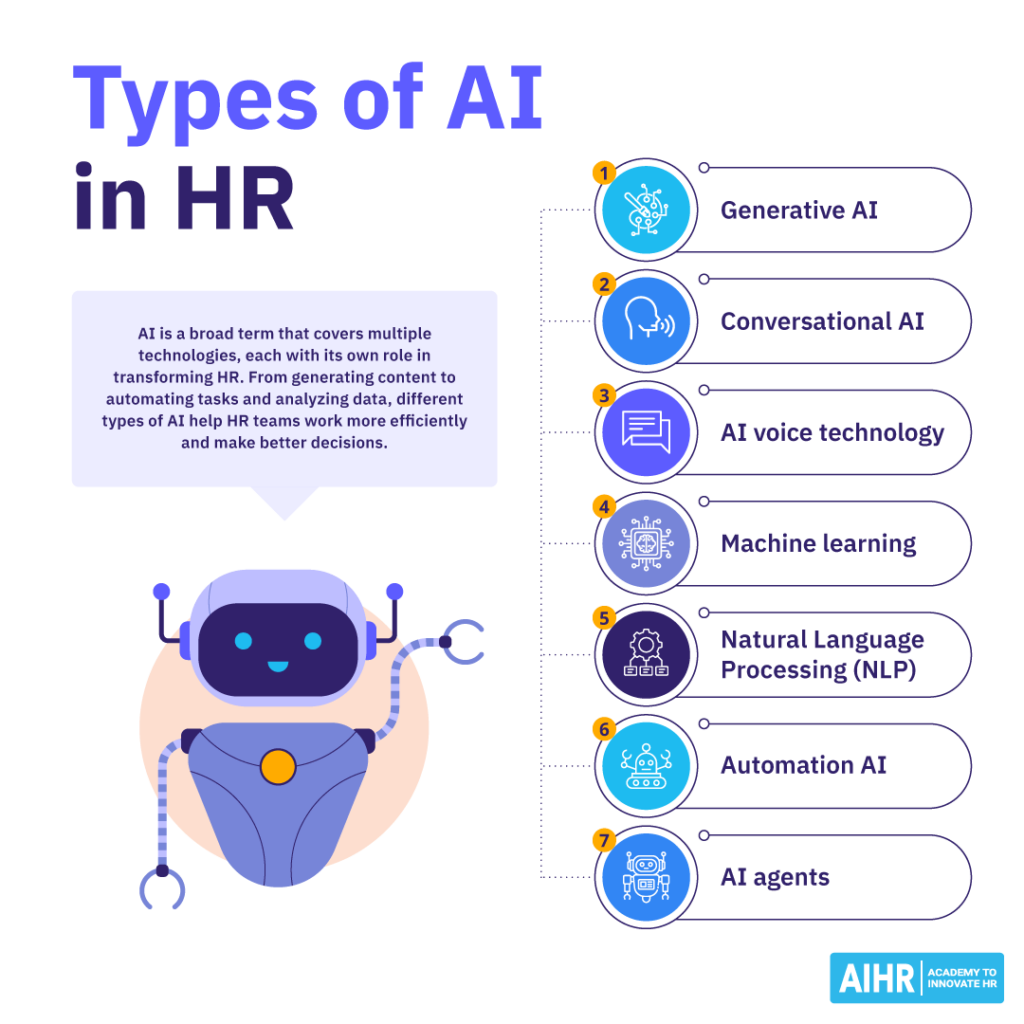
AI has different subsets and types, each with varying purposes, and can be used to complete or support a range of tasks.
Here are some of the different types of AI in HR and what they’re used for.
- Generative AI: Generative AI uses large datasets to create new content, such as text, images, and video. HR practitioners can use it to generate personalized candidate outreach, craft job descriptions, create learning materials, and assist with workforce planning by providing insights into complex data sets. Widely used generative AI tools include ChatGPT, Copilot, and Perplexity.
- Conversational AI: HR chatbots and virtual assistants powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) help HR teams provide instant, 24/7 support to employees and candidates. These AI tools can answer HR policy questions, guide employees through benefits enrollment, offer personalized learning recommendations, and enhance engagement by making HR more accessible.
- AI voice technology: Virtual HR assistants like Grace use AI voice technology to offer 24/7 support, manage inquiries, and escalate more serious issues to a real person, improving the overall response times and accessibility.
- Machine learning: Machine learning enables AI to learn from data and improve over time. In HR, it can predict which employees might leave, match candidates to jobs, and recommend fair salary ranges. Some machine learning models are trained with specific examples (supervised learning) to make predictions, like whether a candidate is a good fit for a role. Others find patterns in large datasets without prior instructions (unsupervised learning), helping HR uncover trends such as why certain teams have higher turnover.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): A type of AI that helps interpret written and spoken languages and can be used in HR to analyze employee surveys and sentiment in feedback, performance reviews, and even interview transcripts. Identifying trends in employee sentiment allows HR teams to proactively address workplace concerns.
- Automation AI: Automation AI helps HR teams outsource repetitive administrative tasks, such as screening resumes, processing payroll, and tracking compliance. This reduces the risk of human error and improves accuracy and efficiency.
- AI agents: An emerging type of AI where autonomous systems can take action, make decisions, and perform HR tasks with minimal human intervention. In HR, AI agents can proactively monitor employee performance, suggest career development opportunities, schedule learning programs, and even guide new hires through onboarding processes.
How is AI used in Human Resources?

AI is reshaping HR by making processes smarter and faster. From analyzing workforce data trends to improving talent management and employee development, AI is helping HR teams work more efficiently while enhancing the employee experience. Whether it’s automating routine tasks or supporting business decisions, AI is becoming an essential tool across the employee lifecycle.
Here’s how HR departments are applying AI in practice.
Recruitment and hiring
Recruitment and hiring were some of the first areas where AI was applied to improve processes. Subsequently, AI has been incorporated into various parts of the recruitment process, from sourcing and pre-selection to interviewing and developing fair compensation. For example, AI-driven applicant tracking systems (ATS) can be used to scan resumes to identify key qualifications and match candidates to job descriptions.
ChatGPT is also useful in recruiting. Recruiters and talent acquisition professionals can use ChatGPT for various tasks across the stages of the hiring process, including:
- Writing job descriptions and job postings
- Boolean string generation
- LinkedIn posts
- Providing pre-interview briefings to candidates
- And so much more.
Onboarding and offboarding
Great employee onboarding can improve retention by 82%. AI-driven onboarding platforms can support organizations and HR in creating an engaging experience for their employees by ensuring the necessary forms are filled in, relevant policies are shared, and training sessions are scheduled. For example, Levity enables organizations to automate their entire onboarding workflow with the help of AI.
Offboarding is no different. When an employee leaves the company, an AI-powered solution can, for example, send out an exit survey, documents related to the return of company assets, and emails to revoke the employee’s access to various systems. Introist provides an automated employee offboarding experience including notifications, personalized communication, and scheduling exit interviews.
Turn AI into your HR advantage
AI isn’t here to replace HR professionals—it’s here to enhance their impact. Whether it’s automating administrative tasks, optimizing recruitment, or improving workforce planning, using AI in HR can help you work more effectively and with more impact.
AIHR’s Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program teaches you how to apply AI in real-world HR scenarios. Gain hands-on experience with generative AI and create an AI strategy that brings results.
Workforce planning
AI can also be very useful in workforce planning. Analytics platforms equipped with AI capabilities can crunch vast amounts of employee data to uncover trends, predict turnover, and highlight potential skills gaps. This, in turn, enables HR professionals to develop targeted training programs and solid succession plans so that their workforce is ready to meet future business needs.
Quinix, for example, has created an AI-powered forecasting and automation solution that lets companies analyze thousands of data points to anticipate peak and down periods in demand and automatically schedule the exact number of employees they need.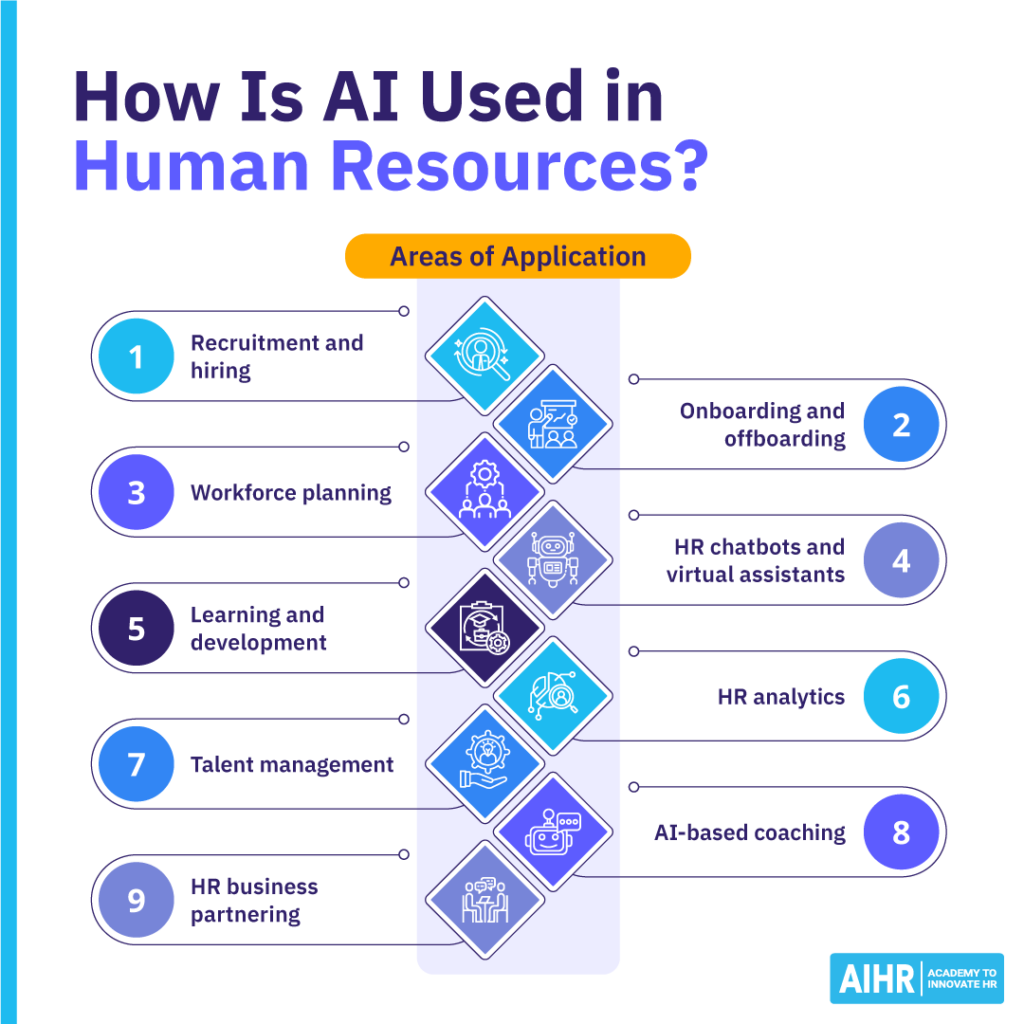
HR chatbots and virtual assistants
Chatbots and virtual assistants are among the more commonly known types of artificial intelligence in HR. A chatbot that serves as an HR assistant can respond 24/7 to employee queries about, for example, leave policies and benefits.
These simple tools can improve an organization’s overall employee experience while saving HR teams from answering frequently asked questions or providing commonly requested information.
DRUID has developed conversational, AI-driven agents that can support HR teams with various processes, including recruitment and onboarding, compensation & benefits, and admin tasks.
Learning and development
There are also various applications of AI in learning and development. For example, AI can enable personalized learning experiences for each employee. AI tools can analyze the learner’s performance and adapt the curriculum or content to their needs and preferences.
Other examples include automated learning content creation, predictive analytics, and intelligent tutoring systems. Novoed has created an AI system that can personalize the learning experience for teams. It analyzes learners’ profiles, preferences, and activities and gives employees tailored course recommendations to map their unique needs and interests. The tool also has AI-driven chatbots that offer learning support.
AI in HR analytics
AI in HR analytics enables organizations to gather and analyze large data sets on employee performance, engagement, turnover, and culture, identifying key areas for improvement. This allows businesses to make more informed data-driven decisions about managing their workforce.
For instance, AI can help HR predict turnover by analyzing past exits, performance trends, and sentiment data. If patterns indicate that employees who lack mentorship are more likely to leave, HR can refine its retention strategy by introducing structured mentorship programs or career growth plans.
AI can also help with compensation benchmarking by analyzing industry salary data and internal pay structures to ensure competitive and equitable salaries. That way, HR teams can address pay gaps and improve retention by offering better compensation packages.
ChatGPT has also emerged as a useful AI tool for people analytics, enabling HR teams to process data, summarize trends, and suggest key insights without requiring coding or advanced technical skills. With ChatGPT and other generative AI tools, HR professionals can identify patterns and make decisions based on data, all without relying on data scientists or complex analytics tools.
AI in talent management
AI is improving talent management by making performance tracking, career development, succession planning, and retention strategies more precise and data-driven.
For example, AI can measure key performance indicators (KPIs) like task completion rates, response times, and peer feedback to provide real-time insights into an employee’s strengths and areas for improvement.
Career development and internal mobility are also great AI in HR use cases. Platforms like Gloat and Eightfold AI recommend internal job opportunities, mentorship pairings, or upskilling programs based on an individual’s experience and aspirations. This helps HR match employees with growth opportunities that align with both personal career goals and company needs.
By integrating AI into talent management, HR departments can track performance with real-time data, personalize career development, identify future leaders, and proactively address retention risks—all leading to a more engaged and strategically managed workforce.
AI-based coaching
AI-based coaching is a technology-assisted coaching process that uses artificial intelligence to provide personalized feedback, guidance, and development support to employees.
- AI-supported coaching uses AI-based assessments to test skills and knowledge and AI-driven tools that provide information to the real-life coach to improve the mentoring relationship. This makes the coach more effective and improves the quality of the coaching sessions.
- AI-augmented coaching enables coachees to utilize AI-based tools between sessions with their human coach, promoting further development, offering continuous coaching, and making the coaching process more scalable than traditional models.
- With the AI-as-the-coach practice, coachees only engage with AI, and they have limited or no interaction with a human coach. This process makes coaching more accessible and scalable.
AI for HR business partnering
As generative AI evolves, it will enable HR professionals to successfully align HR objectives with the strategic objectives of the business. While AI has primarily been used to automate repetitive HR tasks, its potential extends far beyond basic automation to supporting more complex, strategic HR functions.
To maximize AI’s impact, HR professionals need to develop analytical and digital skills to interpret AI-driven insights and integrate them into business discussions. AI enhances decision-making, but HR remains critical in ensuring that strategies are people-centered and aligned with organizational goals. Effective use of AI allows HR to become a true business partner, directly shaping workforce strategies that drive success.
Benefits of AI in HR

Artificial intelligence in HR offers numerous opportunities to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and create more personalized employee experiences. Let’s explore some of the key benefits AI brings to HR.
Improved efficiency and productivity
With AI taking on repetitive administrative tasks, HR teams have more time to focus on more strategic tasks that add value to the business. An example of this in action is at Unilever, where the company had to sort through more than a million applications each year. Using machine learning tools to analyze videos and responses by applicants, they streamlined their hiring process. Unilever’s time-to-hire was reduced by 75%, and they reported a notable increase in the diversity of candidates.
Artificial intelligence in HR can also improve employee efficiency and productivity. For example, managers have access to more data to see what employees have achieved and give more helpful, detailed feedback, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
General Electric (GE) has implemented an AI tool called “Wingmate,” developed in collaboration with Microsoft, to enhance employee performance and productivity. Wingmate assists employees by summarizing manuals, resolving quality issues, and drafting communications. Within three months of its launch, Wingmate was queried over half a million times, indicating significant employee engagement.
Better structured processes
AI in Human Resources is a valuable tool for streamlining and structuring processes, for example, helping you deliver a personalized, seamless onboarding experience for new hires. This includes:
- Automatically creating, sending, and managing digital documents
- An instant messaging system to field questions around the clock
- Analytics to assess the performance of new employees
- Real-time compliance monitoring to make sure required training is completed and documents submitted
- Offering customized training paths related to new hire’s competencies and role
- Creating valuable reports that identify trends in your onboarding workflow.
A global professional services firm collaborated with JIFFY.ai to automate 80% of its onboarding activities. This automation made the process faster and more seamless, improving the overall experience for new hires and allowing the HR team to focus on strategic tasks.
Reduced costs
Automation of repetitive, routine tasks and improved workforce planning can result in significant cost savings. For instance, a leading quick-service restaurant chain partnered with Intelmatix to optimize its staff scheduling process. The AI-powered workforce scheduling solution minimized staff overtime expenses and idle hours by 25%. This optimization ensured that the right number of staff was allocated to meet hourly demand, resulting in better customer service and reduced unnecessary labor costs.
Manipal Health Enterprises implemented MiPAL – a virtual assistant that automatically responds to queries from employees regarding leave, payslips, and other issues – which reduced new hire turnover by 5% annually, and saved over 60,000 hours for employees and the HR team. This ultimately led to substantial cost savings for the company.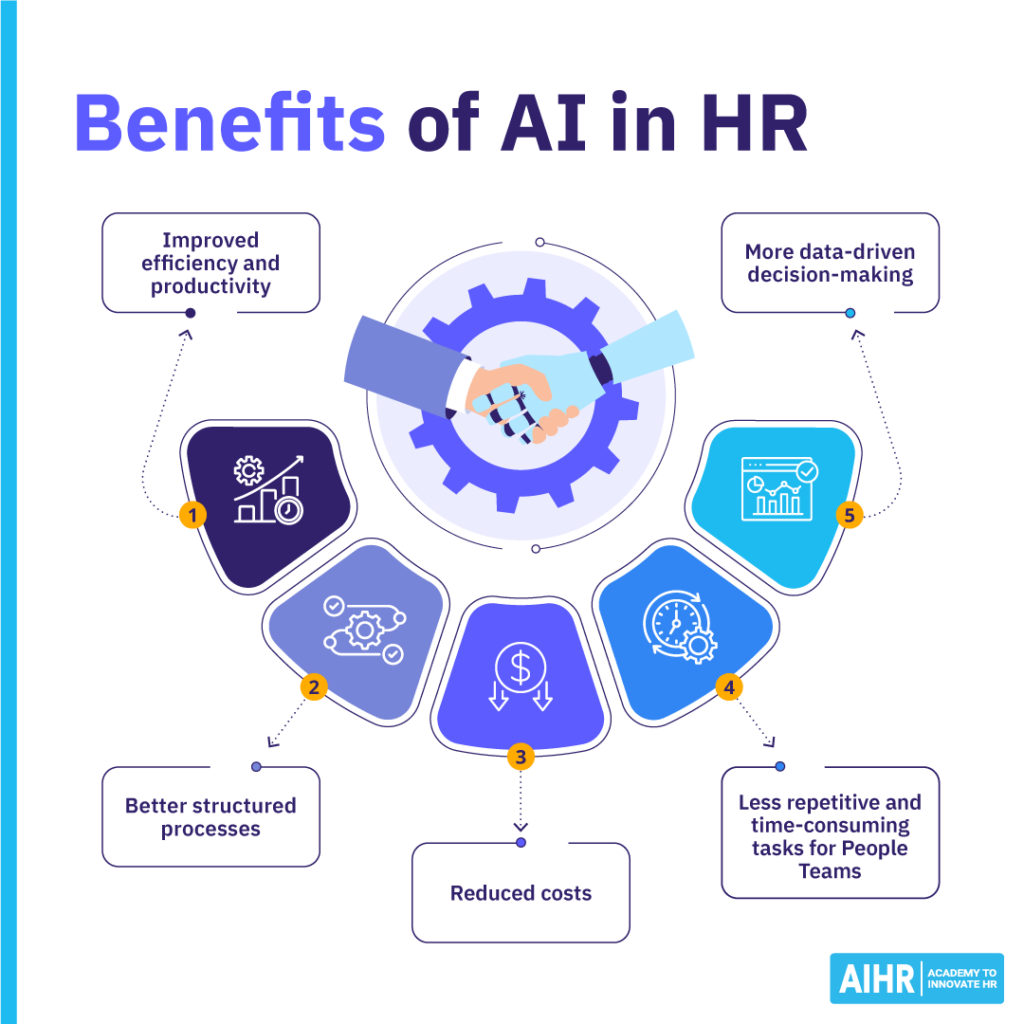
Less repetitive and time-consuming tasks for People Teams
AI is able to serve as a brilliant digital assistant that takes care of manual, time-consuming HR tasks (helpdesk support, scheduling meetings, creating documents, etc.), freeing up their valuable time for more important work that drives the business forward. HR professionals can then focus on creating a more positive, welcoming workplace where everyone feels heard and appreciated, leading to greater efficiency and a thriving culture with strong human connection.
Ambassador Cruise Line used SageHR to automate tasks like reporting, shift scheduling, and booking leave so that the HR team could focus on more strategic efforts. Meanwhile, Mastercard was able to reduce friction in interview scheduling by partnering with Phenom and using AI scheduling, which led to an 85% faster scheduling, with 88% of interviews scheduled within 24 hours of request.
More data-driven decision-making
AI helps HR identify top talent in their workforce, close skills gaps, anticipate turnover risks, and effectively manage talent for the future. With this knowledge, HR can prepare and plan for likely outcomes and adjust talent management strategies based on the organization’s current needs and long-term objectives.
RingCentral partnered with Findem’s talent search solution to combine trillions of external data points with their own internal data to automate candidate matching, outreach, and various other hiring processes. This led to a 40% increase in their pipeline, a 22% increase in quality, and a 40% increase in interest from underrepresented groups.
AI for daily use: ChatGPT for HR

ChatGPT is a popular AI-powered tool that generates text and other content formats, proving to be useful for many tasks in HR.
Here are a couple of examples of how individual HR practitioners can use ChatGPT in their daily work:
- Handling routine HR questions: HR professionals often receive repetitive employee inquiries about policies, benefits, PTO, and payroll. Instead of responding manually to each question, they can use ChatGPT to draft standardized answers or create an internal chatbot that automatically addresses common HR queries, freeing up time for other tasks that require more human touch.
- Writing HR documents more efficiently: ChatGPT can help HR professionals quickly draft job descriptions, offer letters, performance review templates, policy updates, and internal communications. For example, instead of starting from scratch, an HR practitioner can input a few key details and let ChatGPT generate a well-structured job description, which they can then review and customize.
- Supporting the hiring process: HR practitioners can use ChatGPT to analyze job descriptions for biased language, generate interview questions based on role requirements, and even summarize candidate resumes to speed up screening. This can help recruiters focus on evaluating talent rather than spending excessive time on administrative tasks.
- Simplifying HR data analysis: HR professionals can use ChatGPT to summarize key insights from employee surveys, performance reviews, or exit interviews without manually sifting through large volumes of text. For example, instead of reading dozens of exit interview transcripts, HR can ask ChatGPT to highlight common reasons for turnover and suggest potential improvements.
- Improving employee communication and engagement: HR professionals can use ChatGPT to draft clear, engaging emails about company initiatives, policy changes, or engagement programs. It can also assist in brainstorming new ways to improve employee satisfaction, such as suggesting ideas for a recognition program or drafting pulse survey questions to gather feedback.
ChatGPT limitations
It’s important to note that ChatGPT does have some limitations that you must keep in mind when working with the tool:
- Providing incorrect information that looks correct at first glance
- Culturally insensitive or biased answers due to being trained primarily with English/Western data
- Lack of sources and references, which makes it difficult to verify the accuracy of the information provided
- Potential security risks with confidential information being shared via ChatGPT.
Here are some examples of effective ChaptGPT prompts for HR to use.
- “Create a job description for a [ insert name of position ] at a [ insert industry of your company ] company. Include [ A, B, C, D & E ] responsibilities.”
- “List 3 interview questions to test a candidate’s communication skills in a [ insert name of position ] role. For each question, indicate the answer a low-skilled candidate would give and the answer a high-skilled candidate would give.”
- “List 4 frequently asked questions by new hires in a [ insert name of position ] role.”
- “List 5 steps HR should take when creating a competitive compensation strategy for a [ level of seniority ] at a [ size of company ] company in [ location ].”
- “Create an employee exit checklist for HR.”
Adoption of AI in HR: Challenges, adoption personas & best practices
Challenges of AI in HR
While AI’s potential to transform HR is undeniable, it also comes with challenges that cannot be ignored. Understanding these challenges is key to using AI responsibly and effectively in the workplace. Let’s take a closer look.
Inherent risks of AI
AI technology poses direct risks that stem from how it works, its capabilities, and its limitations. These include bias and fairness risks if the technology has been trained on biased data. This can lead to unfair decisions in the hiring process and performance evaluations, leading to legal risks and a less inclusive workplace.
Some AI systems lack transparency regarding decision-making, which can lead to a lack of trust between candidates, employees, and HR, and decisions become hard to justify in legal contexts. When left to operate autonomously, AI technology can behave unpredictably, which can result in incorrect hiring decisions and mismanagement of talent.
Application-based risks
Application-based risks are those that come from the use and application of artificial intelligence systems. In other words, how the technology is used and managed by humans using AI in their work. This includes when AI makes choices that do not align with your company’s values or ethics, which can negatively affect your company culture and decrease morale and trust
For instance, using AI to manage mass layoffs or taking actions without considering essential context (as seen with Uber’s algorithm increasing fares despite market disruptions) can severely harm a company’s reputation and public trust.
Finally, there’s a fine balance to be found between using AI-powered tools and using human insight, empathy, and emotional intelligence. Over-reliance on AI in HR can damage a business’s relationships with its workforce and lead to poor decision-making.
Compliance-related risks
Compliance-related risks come from the legal standards companies are required to adhere to, particularly around data protection and employment laws. AI poses several risks, including data privacy violations when sensitive personal employee data is being collected, used, and stored, discriminatory results (where one group is favored over another based on age, gender, race, etc.), and upholding certain laws that require organizations to properly document how their AI systems work and how they make decisions and ensure these are made fairly and legally.
Failure to manage these risks can result in legal fines and challenges, reputational damage, and the erosion of trust between candidates, employees, and the organization.
The AIHR AI risk management framework
Below is an image of our AI risk management framework, which helps businesses manage these risks across all levels. It comprises four interrelated parts, each one addressing the most significant AI risks.
The first two parts—internal and external environment—focus on organizational internal and external risks. Data governance, the third part, is necessary for addressing both of these risks. The fourth part of the framework outlines the levels—policy and philosophy, practice process and systems, and individual behavior—where these risks must be managed.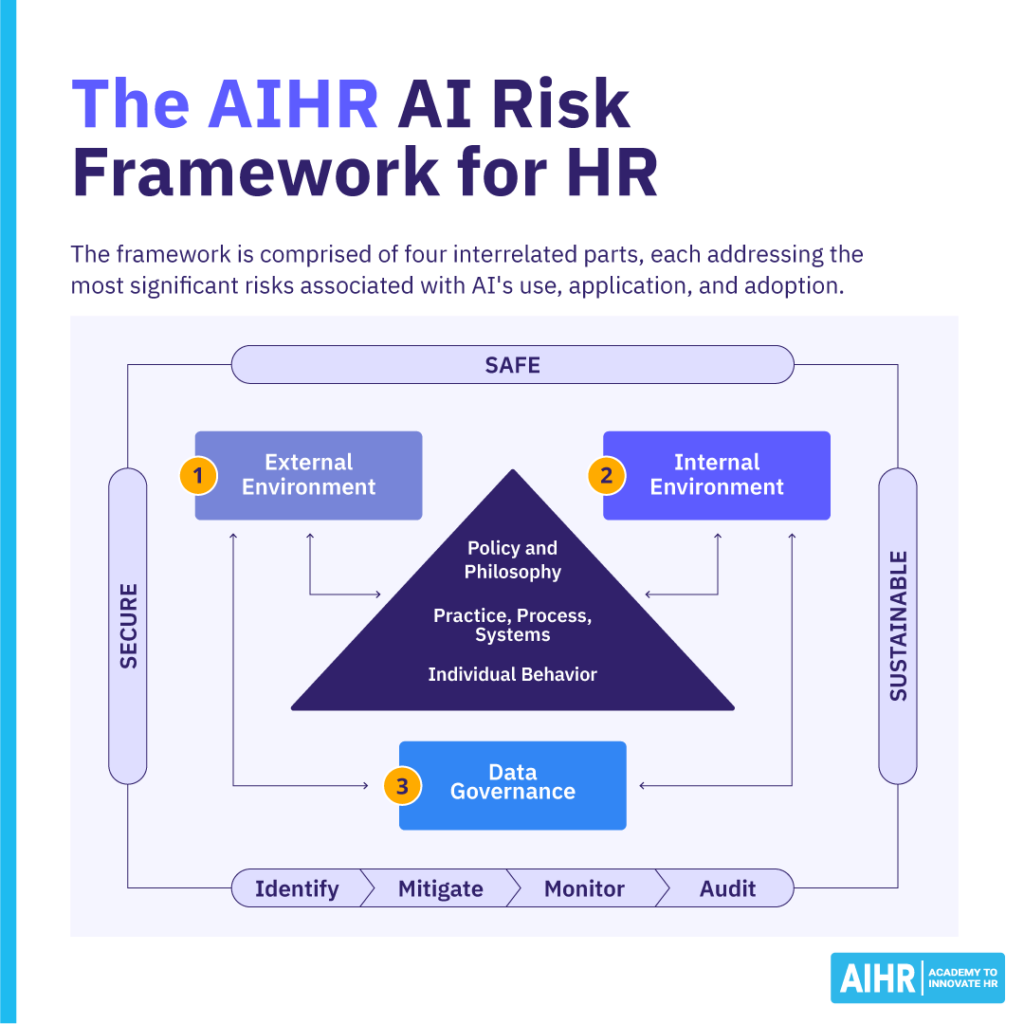
Actions for HR
- Train HR professionals in your team in how to effectively use AI in their day-to-day role, and make sure they know the cases where human input is essential
- Use diverse data to train AI models, adjust algorithms, and reduce bias
- Monitor and conduct regular audits of AI decisions, ethics, and data handling
- Ensure a human reviews AI-driven decisions to check for errors, especially in critical areas like recruitment and performance evaluation
- Opt for explainable AI models where possible
- Be open and honest with candidates and employees about how you use AI to make decisions
- Have data protection policies in place and train employees on these policies
- Only collect and use the data that you need
- Protect sensitive data using encryption and secure access controls
- Work with legal experts to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations
- Maintain detailed records on how your AI systems are used that meet legal requirements
- Ensure AI tools align with company values and ethical guidelines
- Be thoughtful with your use of AI and ensure there is human involvement in more sensitive decisions that require empathy or complex judgment.
The 4 AI adoption personas
HR professionals can be categorized into one of the following four adoption personas. Each persona has different shared behaviors and motivators for (or against) adopting AI, which enables HR to take targeted actions to accelerate adoption across the team and as part of their own learning.
- The Skeptical Avoider: This persona doesn’t actively use AI because they don’t see it as valuable or necessary in their role. Therefore, they lack motivation to prepare themselves for a future where AI is heavily adopted in HR, may hold a negative view towards artificial intelligence in HR, and risk being left behind. The Skeptical Avoider benefits from seeing the value of AI in practical use cases and applications and being encouraged to adopt AI in low-risk day-to-day tasks.
- The Reluctant User: This persona is typically in a workplace where AI is being actively used in daily HR processes, but they use it reluctantly and minimally, usually because they don’t understand it or have trouble integrating it. HR leaders should raise awareness of the benefits of using AI to these users and start with low-risk, high-impact AI applications to build trust.
- The Active Explorer: This persona utilizes AI for tasks such as research, content creation, and task automation. Although they see the benefits of full adoption, they lack opportunities to experiment with AI and lean heavily on self-learning to deepen their knowledge. These users need more opportunities for hands-on practical use of AI and to demonstrate the resulting efficiency gains while getting any concerns that result in hesitancy addressed.
- The Adoption Champion: The final persona actively uses AI across multiple HR practices, including personal productivity and better decision-making, and is eager and willing to experiment with new technologies and tools. They are typically found in companies that make significant investments in AI and help to champion the use of AI in their organizations. HR should leverage these users’ enthusiasm to drive broader adoption of AI across the company, highlight any compelling success stories, and ask for their input on the early adoption of new technologies.
The future of AI in HR

The future of AI in HR not only holds significant promise, but also inevitable transformation within the HR profession. As AI continues to reshape how HR professionals operate, it will be imperative for them to develop new skills to remain relevant and drive business value.
With 76% of HR leaders stating that organizations that fail to adopt AI in the next few years will not be as successful as those that do, it’s clear that AI is changing the HR field. Here are some of the key roles HR professionals will need to play in the AI-powered future and its impact on the HR profession.
1. HR’s role in AI adoption
AI will not only become ubiquitous across the employee life cycle but also form part of the workforce that HR needs to manage. Currently, the workforce consists of traditional employees, gig workers, vendors, or contractors who conduct the work. In the future, HR will also need to manage co-bots working alongside employees to get work done.
Generative AI will be able to take on full responsibility for specific tasks and activities, which will impact work design and how HR develops capacity planning in the future. To manage the workforce of the future, HR professionals will need to understand the value AI bots bring and determine how they can be incorporated into workforce plans.
2. HR’s role will change
As AI removes most of the repetitive, operational work, HR will shift its priority to supporting the adoption of AI across the organization and providing more strategic value to the business.
This will likely mean job displacement for admin-heavy roles. Businesses must think about creating reskilling and upskilling programs to help these employees transition into new roles that consist of tasks and responsibilities that utilize the creativity, empathy, strategic thinking, and emotional intelligence of humans. New, broader roles will emerge that combine business knowledge and technological expertise.
HR professionals will need to develop new skills to adapt to this change. Key skills include:
- Business acumen: Truly understanding the business is the starting point for aligning HR solutions with business needs.
- Communication skills: HR professionals must be able to connect well with all kinds of people and leave a professional and positive impression.
- Delivering through technology: Being able to effectively implement technology into HR solutions to drive efficiency, scale, and business impact.
- Active listening: Active listening goes hand in hand with empathy, the ability to see situations from the perspective of all stakeholders. This is an important skill when navigating the adoption of AI across the business.
- Generative AI skills: Being able to integrate AI into their daily activities and understanding how to work with AI technologies responsible for adjacent tasks.
- Problem-solving skills: Finding new solutions within a digitally enabled workforce that helps the business win in the marketplace.
- Curiosity: Asking questions, staying open-minded, wanting to learn, and being curious.
Not all HR professionals need the same AI skills—what’s required depends on their role and how they interact with AI.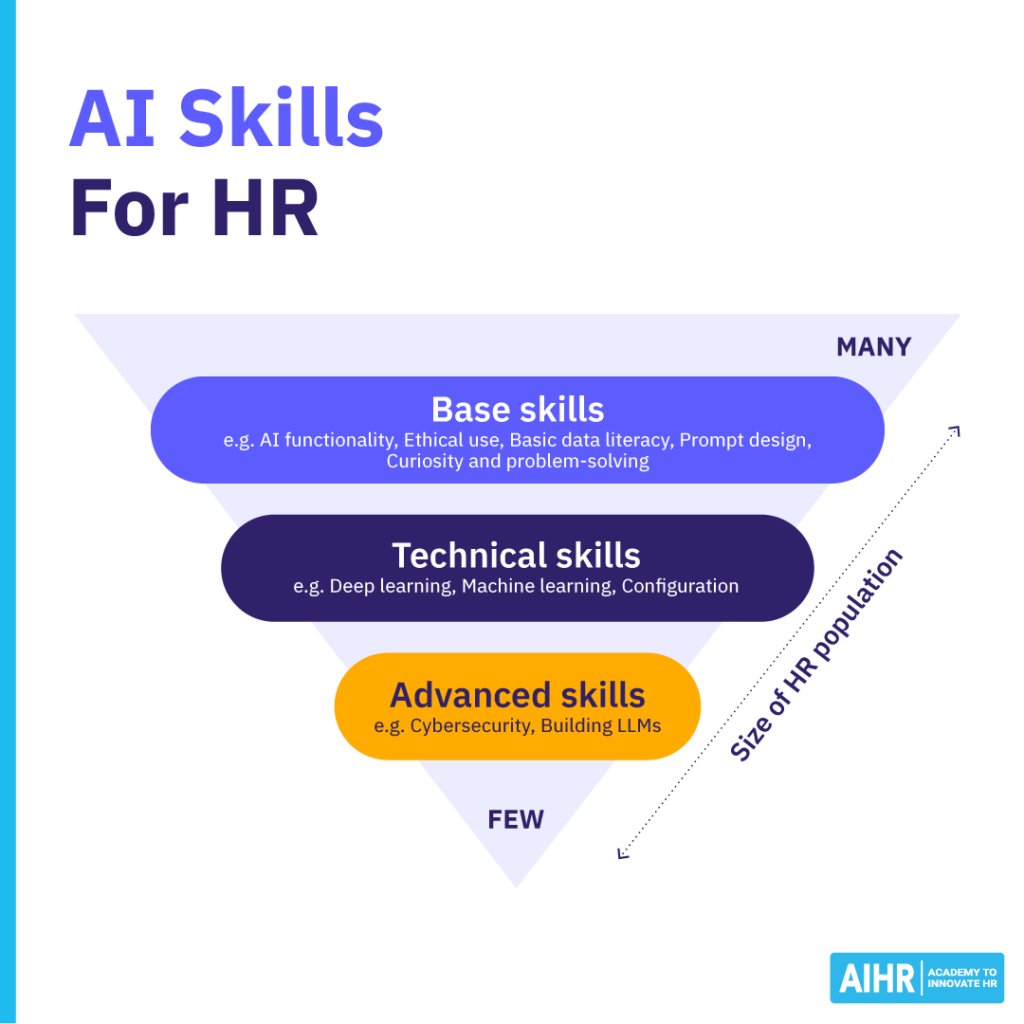
3. Driving responsible AI use
HR will need to become the gatekeepers for responsible use of AI across the organization, now and in the future. In addition to the actions listed above, there are several ways that HR practitioners can contribute to a responsible adoption of AI:
- Assemble a task team to develop guardrails and guidelines
- Experiment with the use of AI, but do so incrementally
- Build trust and transparency in the technology, but be aware of its limitations
- Contribute towards the bigger discussion on the AI future.
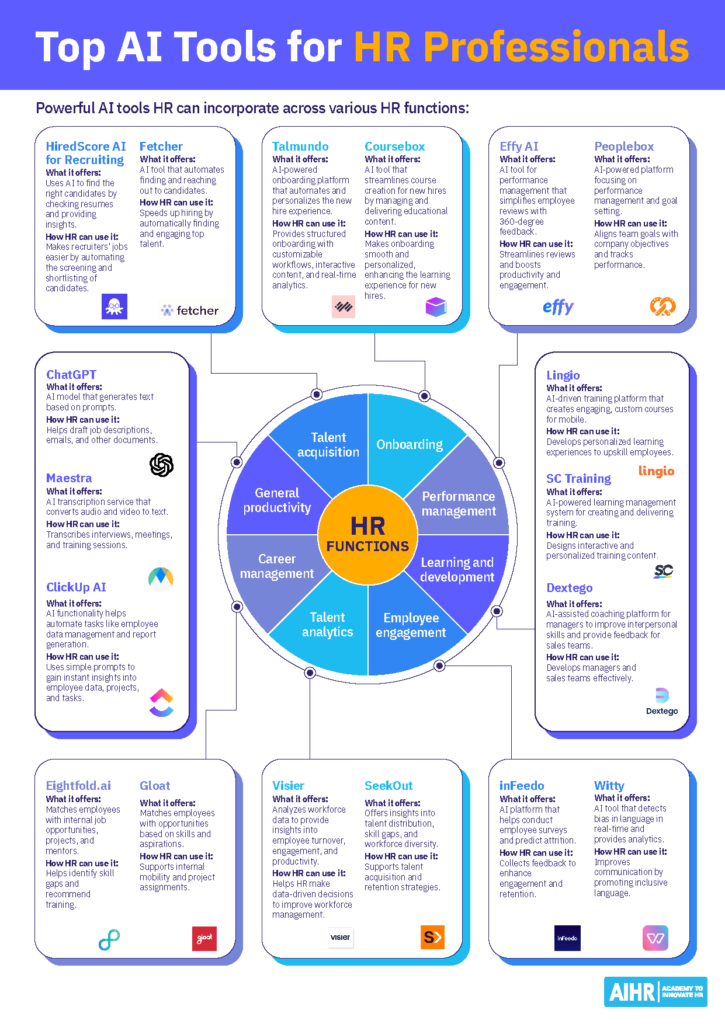
AI tools for HR

Here are some leading AI tools for HR teams to test out across various HR functions.
Will AI replace HR?

According to research by Personio, 61% of business leaders believe HR will be taken over by AI in the future, and many employees in these roles share their concerns. But are their beliefs grounded in facts, or is this a simple case of business leaders not having a clear understanding of what exactly their HR teams do, and the value they provide?
As we’ve already discussed, HR is already changing and will continue to change as AI tools develop and are utilized in a greater way across HR processes. AI will undoubtedly be an asset as it reduces repetitive tasks, but it will not be able to replicate the real relationships and in-person connections that HR teams nurture. Jobs consisting solely of significant simple, repetitive, administrative tasks are likely to be automated, but roles that require more problem-solving and human interaction – which is most HR roles – are far less likely to be automated.
Here are some of the most common HR roles divided into three categories from high-risk to low-risk:
- High-risk: HR Administrators, DEIB Consultants, and Payroll Team Leads.
- Moderate risk: L&D Specialists, HRIS Analysts, and HRBPs.
- Low risk: Senior HRBPs, HR Specialists, and Data Scientists.
For HR professionals who do fall into the high-risk category, there are steps you can take to make yourself a more valuable asset, including upskilling or broadening your skills, learning how to apply your skills in different contexts, and considering moving into a role that requires more critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
But contrary to many beliefs, HR is going to become more important to the business, even as AI adoption grows. In fact, 73% of business leaders believe this to be true. Why? Because once the repetitive, low-value tasks are taken care of, HR teams will be able to focus on more business critical matters, including fostering a great workplace culture, increasing retention, and working directly with business leaders to meet long-term organizational goals.
So, it’s important that HR teams start showing business leaders the value they bring to the table, and equally critical that business leaders invest time in understanding the value HR provides. Every organization is driven by its workforce, which means that people are your greatest asset, and HR’s primary focus is on building and developing relationships with those people.
Artificial intelligence for HR certification
An HR certification can help practitioners build AI knowledge and skills and facilitate real-world applications.
AIHR’s accredited Artificial Intelligence for HR Certificate Program includes hands-on learning to help build, practice, and apply AI skills in HR. The program covers:
- Introduction to AI for HR
- Mastering prompt design
- Using generative AI in HR
- AI strategy for HR.
With a mix of video lessons, hands-on exercises, and assignments, AIHR caters to all learning styles. Plus, all programs are 100% online and self-paced, which means AIHR members can learn at their own pace around their existing commitments.
AIHR’s Resources Library also contains off-the-shelf templates, playbooks, guides, and tools that serve as a great starting point and are included in the course subscription. Our AIHR Copilot is trained on AIHR’s 1,000+ articles, 500+ hours of video lessons, and 100+ downloadable resources, and is there to give you fast, trustworthy, expert-level answers to your burning HR questions. You’ll also become a part of our thriving community of 5,000+ ambitious HR professionals from all over the world, where you can have thoughtful discussions, share ideas, and build genuine connections.
Full access members will also receive a personal coach who will assist and help them reach their learning goals and career potential.
FAQ

Through generative AI, HR chatbots, AI voice technology, natural language processing, automation, and AI agents, artificial intelligence is able to complete repetitive HR tasks, assist in decision-making, mimic human creativity, comprehend questions and provide helpful answers on demand, predict outcomes, and interpret written and spoken languages all with minimal human input. This makes it useful in HR functions across the employee life cycle.
AI can help HR in numerous ways, and this capacity is only set to grow as the technology evolves. The main benefits include improving efficiency and productivity, streamlining and structuring processes, reducing time-consuming tasks and costs, and facilitating more data-driven decision-making.
The best AI tool for HR depends on what your needs and goals are. You’ll find AI tools across all HR functions, including talent acquisition, onboarding, performance management, learning and development, employee engagement, talent analytics, career management, and general productivity. Many AI tools offer trials and integrate seamlessly with your existing HR tech stack.
Generative AI helps HR create valuable materials, including text, images, and video, by analyzing large datasets and generating original content. This technology can be used to draft compelling job descriptions, create personalized outreach emails and rejection letters, serve as virtual onboarding assistants, provide customized learning and development suggestions for employees, uncover key patterns and insights in data, and much more.